You came to the indicated post to see an overview of the Workload Domain in VCF. Let’s start with an conceptual introduction…
From a Cloud Foundation perspective, a workload domain is a logical SDDC instance of one of more vSphere clusters with a dedicated vCenter server and a NSX Manager which are both located in the management domain. Workload domain provisioning is automated through SDDC Manager which will configure vCenter, vSphere, vSAN, and NSX and will enable integration with any installed vRealize suite components.
Cloud Foundation supports a total of 15 Workload Domains (WLDs) within a deployment. Each vCenter server deployed within each workload domain is configured with enhanced link mode and they all share a common SSO domain with two platform services controllers.
A common question from customers is whether they will need to purchase a separate vCenter licenses for each Workload domain vCenter server. The answer is no. The single vCenter license that is entered in the deployment parameters spreadsheet will support all vCenter instances within the deployment.

Policy managed infrastructure for workloads
Workload domains are on-demand policy managed infrastructure for customer application workloads. Each workload domain is a logical self-contained SDDC instance which can be managed using software defined policy. They are configurable with the customer’s choice of supported hardware, they can be created, expanded, deleted and upgraded independently of other workload domains.
Workload domains can be configured with multiple clusters which scale to the full limits of vSphere and vCenter. Cloud Foundation automates the life cycle management, patching and upgrades of each cluster within a workload domain which allows out customers the flexibility to run their environments at different levels.
External storage support is inclusive of vSAN, NFS and Fiber Channel which can be used as principal storage when creating a new VI workload domain. It is a requirement that vSAN be used in the Management domain. Supplementary storage such as NFS, iSCSI or Fibre Channel can also be added to an existing workload domain.

Workload Domain Design
This shows a clear visual representation of the SDDC components which reside within a management domain and which new components are deployed once a new set of Virtual Infrastructure (VI) workload domains are deployed.
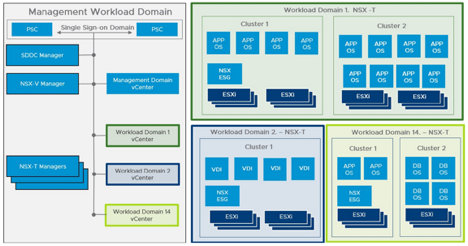
Workload Domain Design with NSX-T
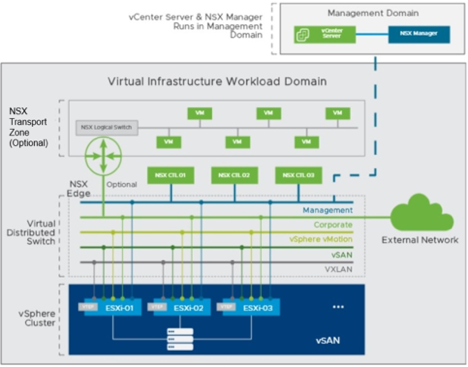
This figure shows a clear visual representation of the SDDC components which reside within a management domain and which new components are deployed once a new set of NSX-T based VI workload domains are deployed.

This figure shows a clear visual representation of the SDDC components which reside within a management domain and which new components are deployed once a new set of NSX-V based VI workload domains are deployed.
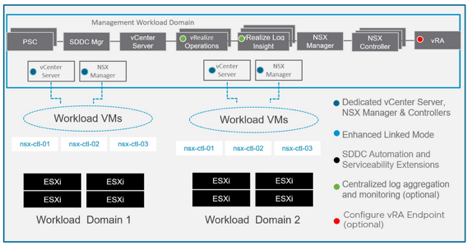
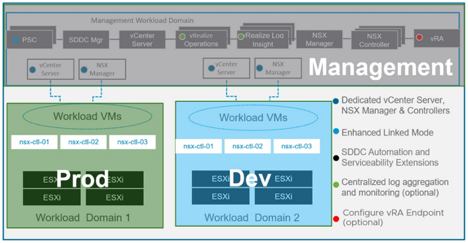
Management Domain
The management domain has a special purpose, there will only be one management domain for each VMware Cloud Foundation deployment.
The management domain is where all the management components run such as SDDC Manager, the management vCenter Server, the two platform services controllers, the NSX Manager and the vRealize Suite. The dedicated vCenter Server and NSX Manager for each workload domain will also be provisioned here and run inside the management domain. vRealize Log Insight is deployed by default by bring-up in the management domain and all components are configured to send their logging to this log insight cluster.
VMware supports running applications inside of the management domain in a consolidated architecture using resource pools. At a minimum, Cloud Foundation supports four hosts. The management domain is built upon vSAN and NXS-V. NFS backed workload domains and or NSX-T based workload domains can be used when additional VI workload domains are configured, but not in the management domain.
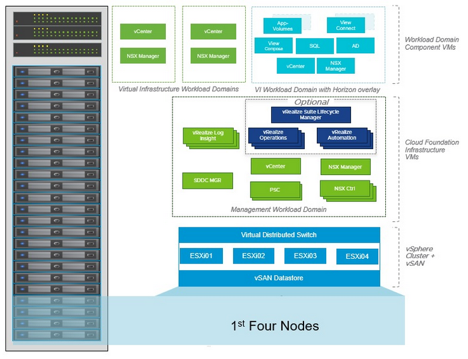
Virtual Infrastructure Domain
Each virtual infrastructure domain requires a minimum of three hosts, although four is always recommended for VSAN.
Each VI domain is a vSphere cluster and will get its own dedicated vCenter server and NSX manager (again deployed inside of the management workload domain). NSX is deployed and ready to use – we do not create any default NSX configurations. We allow the customer to configure their NSX logical networks, routed networks, load balancing and distributed firewall rules and security policies at a per workload domain level in their own time when they are ready.
Sizing of a VI workload domain is based upon user input and the numbers of nodes or failures to tolerate. We recommend using VSAN sizing tools to determine the number of nodes that are needed.
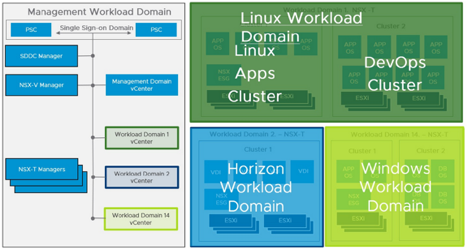
Cloud Foundation supports creating multiple clusters within a domain. This is very useful for running different types of applications within one domain, each cluster can have its own application specific hardware configurations. This allows applications to scale easily to the published vSphere and NSX supported maximums.
Dedicated vSphere Cluster (min of three hosts):
- Separate vCenter Server
- Shared Single Sign-On (SSO) domain with management Workload Domain
- Size calculated based on user inputs
- Can be expanded later
vSAN:
- Support for Hybrid and All-Flash
- Eight disks per controller / five disk groups per host
- One vSAN datastore per workload cluster
VMware NSX:
- NSX Manager deployed in the Management Workload Domain
Automated Workload Domain Deployment from the SDDC Manager Interface
Automated Workload Domain deployment is made easy with VMware Cloud Foundation. With a few clicks and some basic sizing information, SDDC Manager completely automates the process.
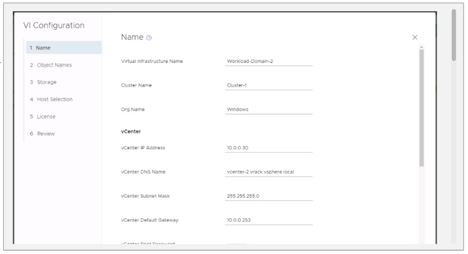
- Select VI-Virtual Infrastructure as Domain Type
2. Changing vSAN Failure to Tolerate (FTT)
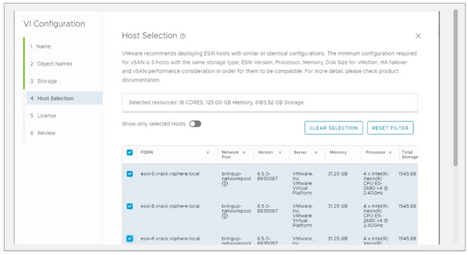
3. Select Servers
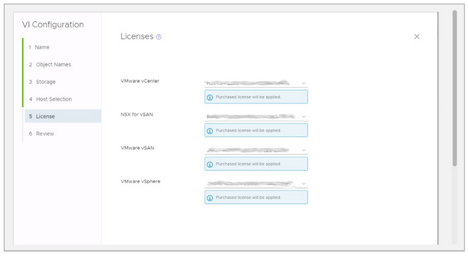
4. License
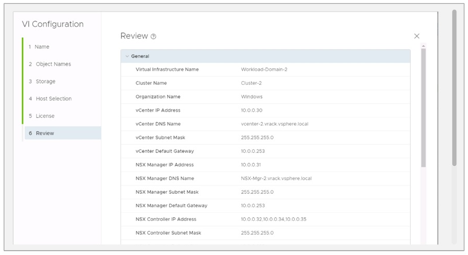
5. Review
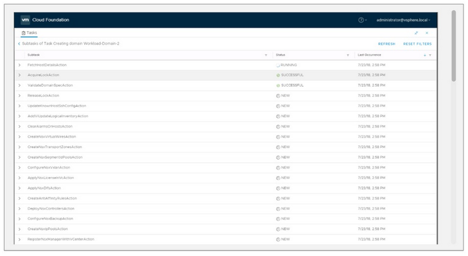
6. Execute Workflow
Closing Note
I hope it has been useful to you. In the next VCF post we will see the types of deployment. See you next!

