What´s up folks! Continuing with the news of vSphere 7, today we will see the enhancements in Cluster.
Cluster Quickstart Workflow
In the vSphere Client, we can use the Cluster Quickstart workflow to create, configure, and expand clusters.
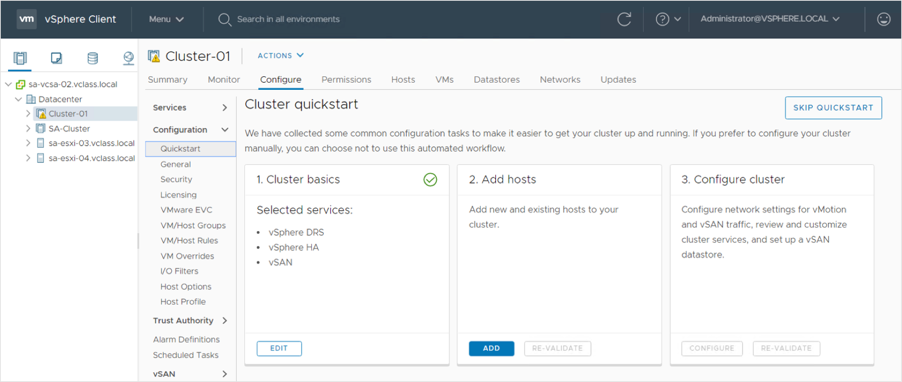
The Cluster Quickstart workflow guides us through the process of deploying clusters. It covers every aspect of the initial configuration, such as host, network, and vSphere settings. Cluster Quickstart reduces the amount of time it takes to configure a cluster.
Creating a Cluster
When we create a cluster, we can enable cluster services:
• vSphere DRS
• vSphere HA
• vSAN
The steps of the Cluster Quickstart workflow vary depending on the selected services.
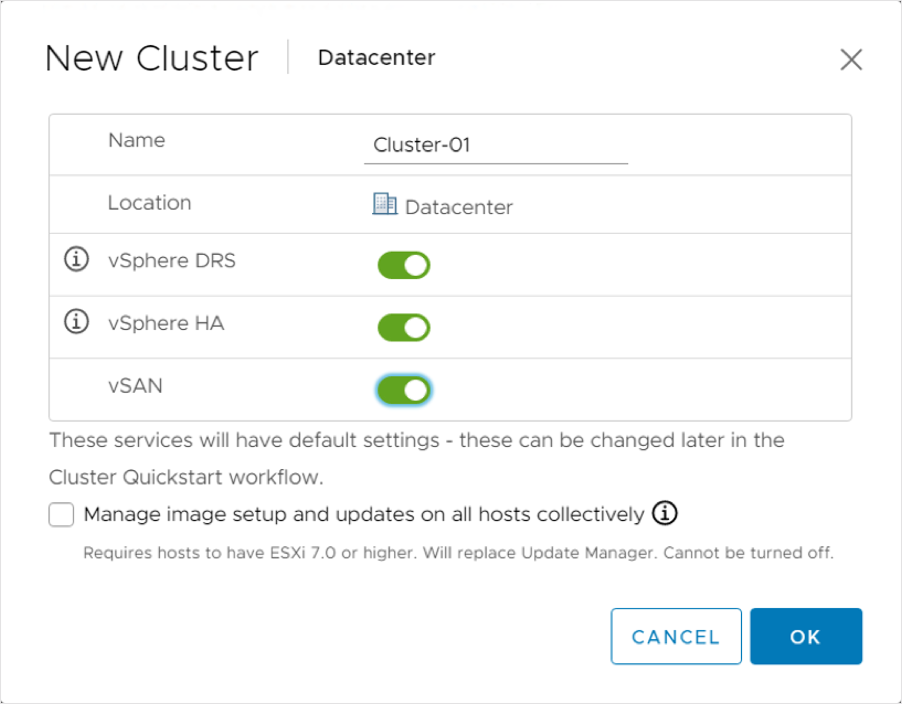
Using Cluster Quickstart Workflow to Add Host
On the Cluster quickstart page, we click Add to add hosts to our cluster.

We enter the IP address or FQDN of each host that we want to add to the cluster. From the inventory, we can also select existing hosts that are not part of a cluster.
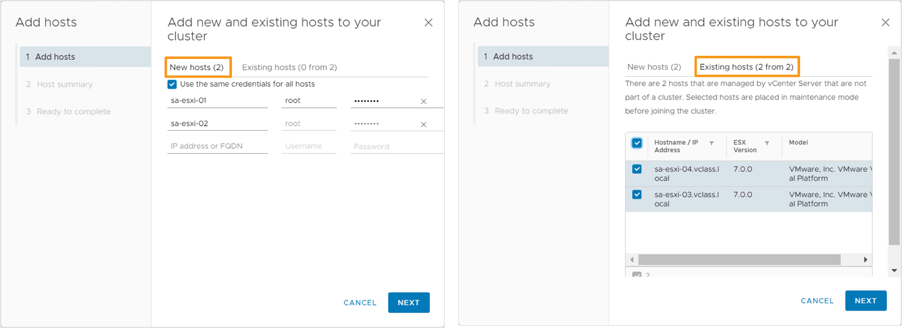
By selecting the Use the same credentials for all hosts check box, we can streamline the process of adding hosts to the cluster. If the system cannot validate a host, we are prompted to manually validate its certificate and accept its thumbprint in the Security Alert pop-up. The Host summary page lists all hosts that are added to the cluster and related warnings.
Using Cluster Quickstart Workflow to Configure a Cluster
To configure the host networking settings and services on our cluster by using the Cluster Quickstart workflow, click CONFIGURE.

If we click SKIP QUICKSTART, we can manually configure our cluster by using the menus in the vSphere Client. By skipping the Cluster Quickstart workflow, we cannot restore it. Any hosts added to this cluster must be configured manually.
Configuring a Cluster: Distributed Switches
Using the Cluster Quickstart workflow, select up to three distributed switches. When we enable vSAN, default networks are created for vSphere vMotion and for vSAN. When creating a distributed switch, select at least one physical adapter.
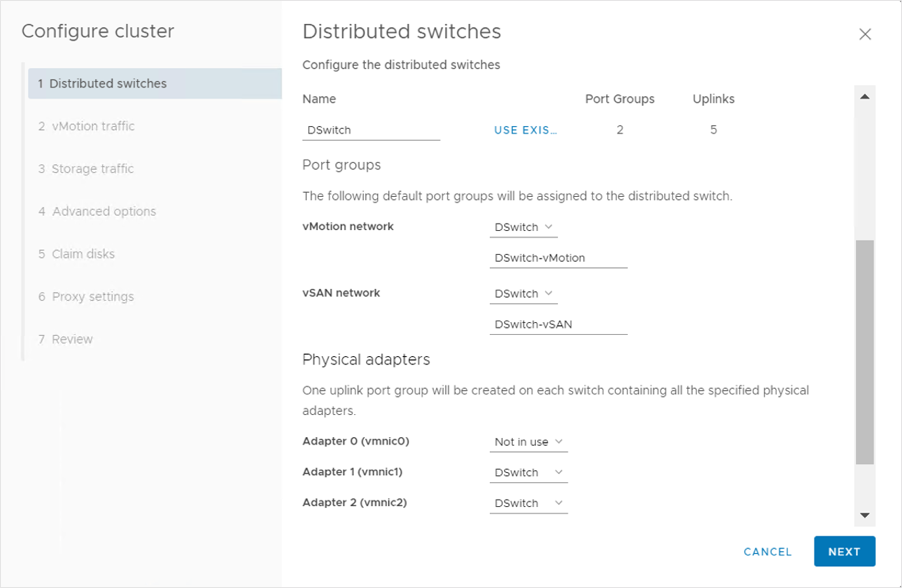
Alternatively, we can select the Configure networking settings later check box to configure the default settings only for the cluster services and to hide all options that are related to host networking. But, by selecting this option, we cannot perform the networking configuration by using the Configure cluster wizard.
Configuring a Cluster: vMotion Traffic
On the vMotion traffic page, we enter the IP address information for the vSphere vMotion traffic.
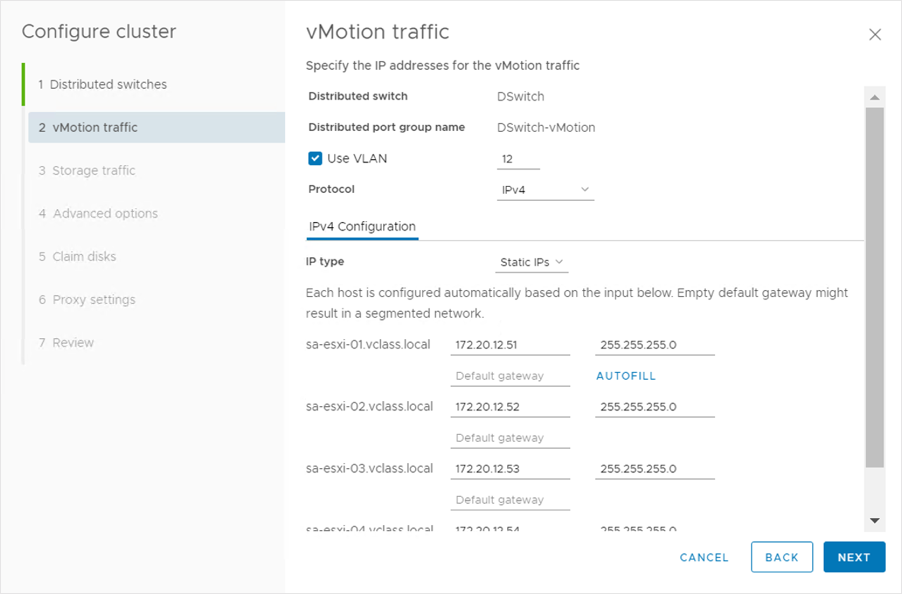
We enter the information for the first host and click AUTOFILL to complete the fields for the following hosts.
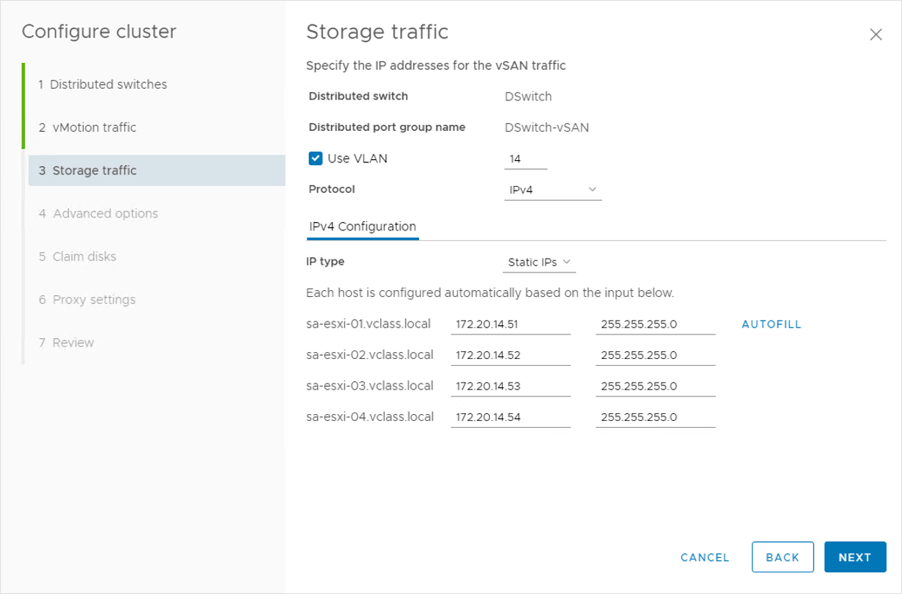
Configuring a Cluster: Storage Traffic
On the Storage traffic page, we enter the IP address information for the storage traffic.
Configuring a Cluster: Advanced Options
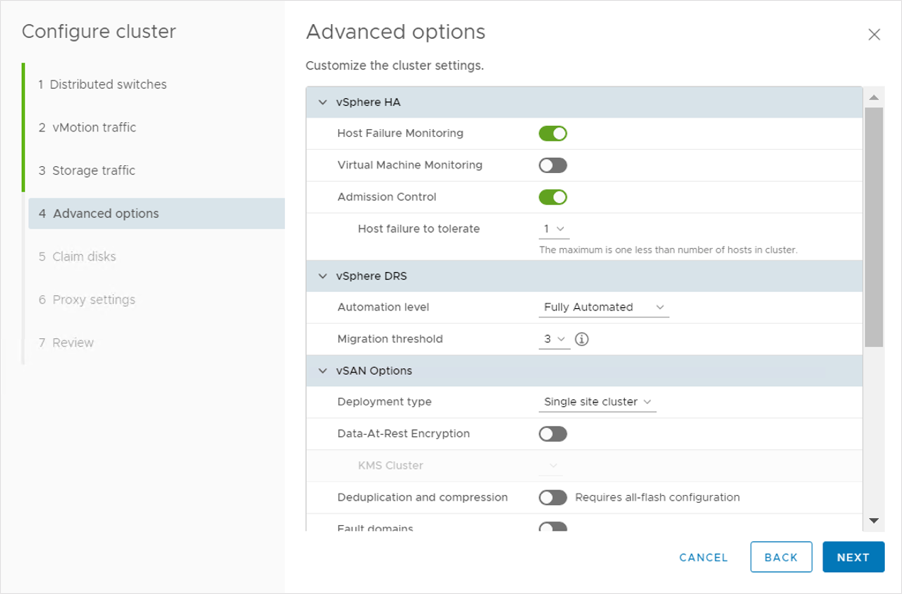
On the Advanced options page, we get different settings depending on the cluster services that are enabled:
• High Availability (optional)
•Distributed Resource Scheduler (optional)
• Host Options
• Enhanced vMotion Compatibility
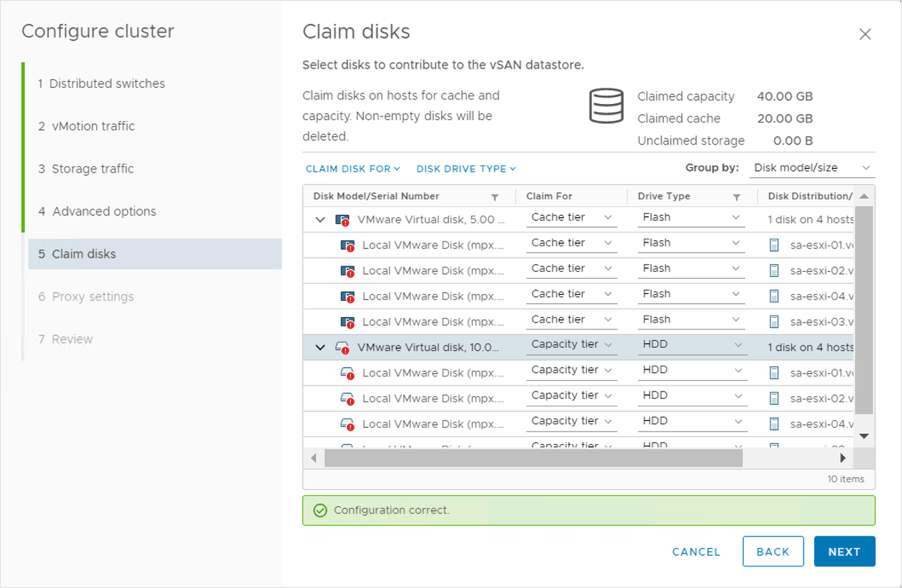
Configuring a Cluster: Claim Disks
On the Claim disks page, we can claim cache and capacity disks for vSAN on each host. We manually create disks groups after the cluster is created.
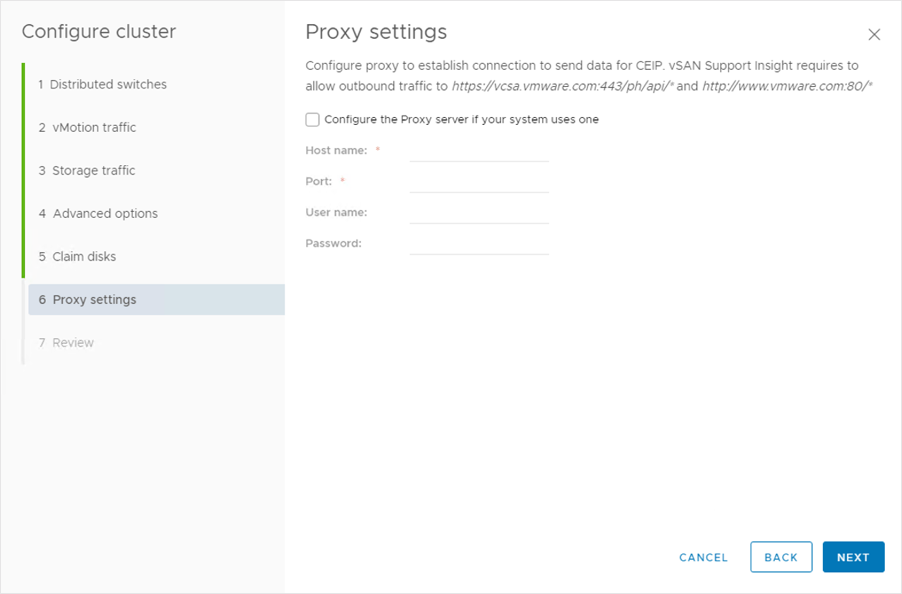
Configuring a Cluster: Proxy Settings
To send data for the Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP), configure a proxy server.
Additional Cluster Configuration
After we complete the Cluster Quickstart workflow, we can configure additional settings, review and customize cluster services, and set up a vSAN datastore.
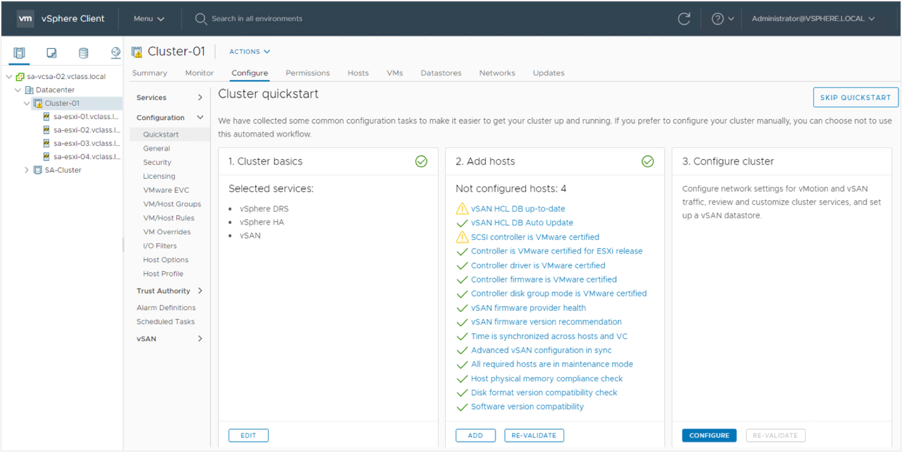
The Cluster Quickstart workflow uses the vSAN health services to validate the configuration and to help us correct configuration issues. It performs checks and makes recommendations according to VMware best practices to help ensure the highest levels of stability and performance.
Using Quickstart to Expand Cluster
We can quickly expand an existing cluster while maintaining consistency and adhering to VMware Validated Design recommendations. For example, we can add hosts to a vSAN cluster, keep the hosts uniformly configured, and avoid disrupting any ongoing operations:
• Apply the existing networking settings.
• Claim disks on each new host.
• Place the new hosts into fault domains.
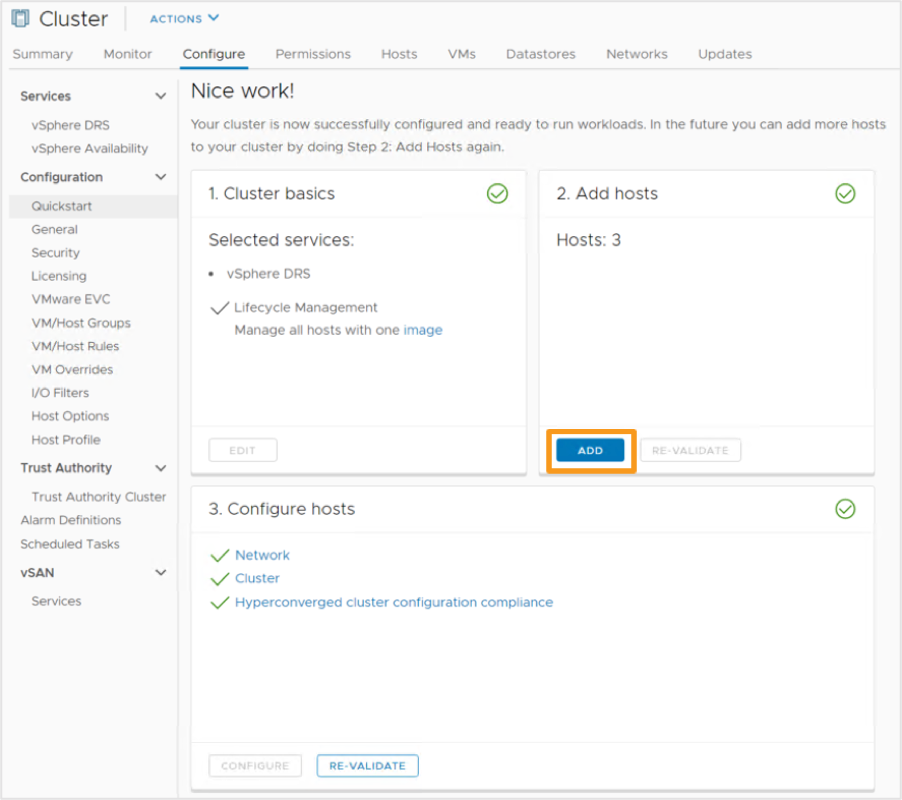
All hosts in a cluster should have the same or a similar hardware configuration. The Cluster Quickstart workflow simplifies the process of keeping HCI clusters consistent.
Closing Note
I hope it has been useful to you. In the next blog we will see the second part, see you!

